 Maryland is divided into two obvious sections by Chesapeake Bay. One section of Maryland lies to the
east of Chesapeake Bay on the Delmarva Peninsula (Name: Delaware, Maryland, Virginia ). This section of the state is referred to as the East
Shore. The section of Maryland that lies to the west of Chesapeake Bay is referred to as the West Shore.
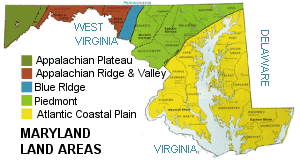
Despite Maryland's small size, five major land areas define the landscape.
Maryland is divided into two obvious sections by Chesapeake Bay. One section of Maryland lies to the
east of Chesapeake Bay on the Delmarva Peninsula (Name: Delaware, Maryland, Virginia ). This section of the state is referred to as the East
Shore. The section of Maryland that lies to the west of Chesapeake Bay is referred to as the West Shore.
Despite Maryland's small size, five major land areas define the landscape.
Atlantic Coastal Plain: The
Atlantic Coastal Plain,
that stretches from New Jersey to Florida, around the Gulf of Mexico, south to Mexico and to the Yucatan Peninsula.
It covers the East Shore and part of the West Shore of Maryland. Maryland lies in an area some refer to as
the
Mid-Atlantic Coastal Plain.
From the northeastern tip of Maryland, the plain extends south and west across Maryland almost to Washington,
D.C. near the Virginia border. The plain is flat and low rising to around 400 feet on the West Shore. Marshy
areas can be found on the East Shore, including the
Pocomoke Swamp.
The West Shore has been used for farming since colonial times, particularly for growing tobacco.
Piedmont: The Piedmont runs from New Jersey, southwest, to Alabama. About 50 miles wide as it cuts
across the state from the northeast through central Maryland, the Piedmont is marked by low rolling landscapes
and fertile valleys. Two ridges, the Dug Hill Ridge (1,200 feet), near the Pennsylvania border and Pars Ridge
(880 feet) run in a southwesterly direction through Maryland. Rivers and streams to the west of the ridges
flow into the Potomac River. Rivers and streams to the east of the ridges flow into Chesapeake Bay. Frederick
Valley, along the
Monocacy River,
to the east of the ridges is a rich dairy farming area.
Blue Ridge Region: To the west of the Piedmont is the Blue Ridge. The Blue Ridge Region extends from
southern Pennsylvania south to northern Georgia. In Maryland, the Blue Ridge is represented by a narrow,
mountainous section of land between the Piedmont and the Appalachian Ridge and Valley. This region,
mostly over 1,000 feet, lies in northern Maryland near the Pennsylvania border.
South Mountain
and
Catoctin Mountain
are in the Blue Ridge Region of Maryland.
Appalachian Ridge and Valley: The Maryland section of the Appalachian Ridge and Valley is the northern strip
of land that separates West Virginia from Pennsylvania. The eastern part of the Appalachian Ridge and Valley
is dominated by the Great Valley (Hagerstown Valley), supporting orchards and farmland. A landscape of
northeast to southwest ridges lies to the west of the Great Valley. Elevations in this mostly forested
area of Maryland reach almost 2,000 feet.
Appalachian Plateau: To the west of the Blue Ridge is the Appalachian Plateau. The Appalachian
Plateau, in Maryland, covers a triangle of land in the westernmost portion of Maryland. The Allegheny Mountains
cover most of this area.
Backbone Mountain,
the highest point in Maryland, is located in this region.
Deep valleys, cut into the plateau by rivers, characterize this heavily forested area.
A Brief Description of the Geology of Maryland from the Maryland Geological Survey.
( Maryland Close-up ) |




