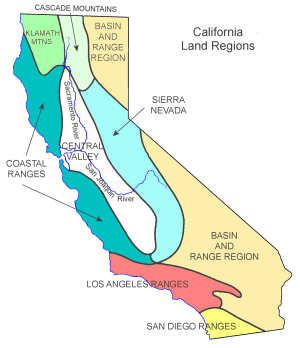
 California is the third largest state, behind Alaska and Texas, and runs almost 800 miles from north to south.
It is not surprising that it offers a
contrasting landscape and a diverse topography.
California's general coastline is 840 miles long. Along much of the coast, the Coast Ranges rise from the shore in steep cliffs and terraces.
Southern California has many wide, sandy beaches. California's topography can be characterized by defining eight main regions
within the state;
California is the third largest state, behind Alaska and Texas, and runs almost 800 miles from north to south.
It is not surprising that it offers a
contrasting landscape and a diverse topography.
California's general coastline is 840 miles long. Along much of the coast, the Coast Ranges rise from the shore in steep cliffs and terraces.
Southern California has many wide, sandy beaches. California's topography can be characterized by defining eight main regions
within the state;
Klamath Mountains: In the northwest corner of the state are the
Klamath Mountains. They are comprised of
many small forest covered ranges and are higher than the
coastal mountains to the south.
Many mountains range from about 6,000 to 8,000 feet above sea level. The small ranges are separated by deep canyons.
Coastal Ranges: The
Coastal Ranges in the north
reach inland 20 to 30 miles extend from the
Klamath Mountains in the north south to Santa Barbara. The Coastal Ranges
include many smaller chains of mountain ranges including the Diablo and Santa Cruz Mountains. Some of the valleys
separating these ranges are the Napa Valley, north of San Francisco and the Santa Clara and Salinas Valleys to the
south. The Coastal Range is home to California's legendary Redwoods and, less fortunately the San Andreas Fault.
The San Andreas Fault enters
California from the Pacific Ocean near Port Arena and extends southeast into the state.
Earthquakes are caused by movement of the earth's crust along this fault.
 |
Yosemite, Tunnel View
Courtesy of Robert Holmes |
The Sierra Nevada: The
Sierra Nevada mountain range in the east
runs about 430 miles from north to south and forming a giant wall rising to over 14,000 feet. The range varies from
around 40 to 70 miles wide. Many peaks in the range reach over 14,000 feet above sea level, with Mt. Whitney, at
14,494 feet, the highest peak in the United States south of Alaska. Mountain streams and glacial action have cut deep valleys into
the western part of the Sierras. Yosemite Valley is one of the most spectacular of these valleys. Visit the
Sierra Nevadas at the United States Geological Survey.
Central Valley: The
Central Valley lies
between the Coastal Range and the Sierra Nevada range and is home to the San Joaquin and Sacramento rivers. Sometimes
called the Great Valley, the
Central Valley is about 450 miles long
from points in the northwest to the southeast. A level, broad fertile plain, the Central Valley is the
most important farming area west of the Rocky Mountains and comprises about three-fifths of California's
productive farmland.
 |
Mount Shasta
Courtesy of Robert Holmes |
Cascade Mountains: The Cascade
Mountains extend north from the Sierra Nevada mountain range. They were
formed by volcanoes unlike the other mountain ranges in California and support one still-active volcano; Lassen Peak.
Lassen is 10,457 feet high and located in the southern Cascades. The Cascade Mountains are also home to Mt. Shasta,
once and active volcano. Mt. Shasta rises 14,162 feet above sea level.
Basin and Range Region: The
Basin and Range Province
contain the southeastern deserts of California. The Basin and Range Region is part of a large region that extends
into Nevada, Oregon, and other states.
In the north, much of the area is a lava plateau. This was formed thousands of years ago when the region was
flooded with molten lava flowing out of cracks in the earth's surface.
In the south, a good deal of the area is wasteland and includes the
Mojave Desert and the
Colorado Desert.
Death Valley lies near the California-Nevada border and features some of the most inhospitable territory in
the world. Some areas of the Basin and Range Region have been made quite productive, however, due to large
irrigation projects that have made farming feasible. Two of these areas are the Imperial and the Coachella Valleys
near the California border with Mexico.
The Los Angeles Ranges: The Los Angeles Ranges, between Santa Barbara and San Diego counties, are a group
of small mountain ranges that extend east to west. Because of this general east-west direction, the Los Angeles
Ranges are sometimes called the Transverse Ranges. Most mountain ranges in California run generally from north to south.
Included in the Los Angeles Ranges are the Santa Ynez, Santa Monica, San Gabriel, and San Bernardino mountains. Sometimes the San Jacinto and Santa Ana Mountains are included as part of the Los Angeles Ranges.
The San Diego Ranges: The San Diego Ranges cover most of San Diego county in the southwestern corner of
California. These mountains, sometimes called the Peninsular Ranges, include the Agua Tibia, Laguna, and Vallecito mountains
and extend southward into the Mexican peninsula known as Baja California.
The general coastline of California is 840 miles long. Much of the coast is characterized by the Coast Ranges rising from the shore in steep cliffs
and terraces. In southern California many wide, sandy beaches can be found.
From the peak of Mt. Whitney to Death Valley, California's topographic diversity is exemplified.
Mt. Whitney, the highest point in the 48 contiguous United States, and Death Valley, the lowest point
in the United States, lie only 85 miles from each other.
Read more about the
major land areas
of California, including the Cascade Range, the Klamath Mountains, and the Mojave Desert. This
interesting overview is provided by the California Department of Conservation.
For more about the Coastal Geography of California, visit
these pages
from the California Coastal Resource Guide by the California Coastal Commission.
( California Close-up ) |




